| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 715. Range Module
- 프로그래머스
- attribute
- Python Implementation
- 30. Substring with Concatenation of All Words
- kaggle
- DWG
- Generator
- Decorator
- LeetCode
- 운영체제
- shiba
- Python
- 109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
- Protocol
- Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
- iterator
- 43. Multiply Strings
- 컴퓨터의 구조
- Regular Expression
- Python Code
- 315. Count of Smaller Numbers After Self
- concurrency
- 밴픽
- Class
- data science
- 파이썬
- 시바견
- t1
- Substring with Concatenation of All Words
Archives
- Today
- Total
Scribbling
LeetCode: 218. The Skyline Problem 본문
아래 너튜버분께 매번 배우게 되는 것 같다.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GSBLe8cKu0s&t=3s
아래는 위의 영상에 나온 알고리즘의 파이썬 코드이다.
from functools import cmp_to_key
import heapq
class Solution:
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
# [loc, height, isEnd]
points = []
for l, r, h in buildings:
points.append([l, h, 0])
points.append([r, h, 1])
def compare(p1, p2):
if p1[0] != p2[0]:
return p1[0] - p2[0]
if p1[2] != p2[2]:
return p1[2] - p2[2]
if p1[2] == 0:
return -(p1[1] - p2[1])
return p1[1] - p2[1]
points.sort(key=cmp_to_key(compare))
ret = []
pq = [0]
for loc, height, isEnd in points:
prevmax = -pq[0]
if not isEnd:
heapq.heappush(pq, -height)
if -pq[0] != prevmax:
ret.append([loc, height])
else:
pq.remove(-height)
heapq.heapify(pq)
if -pq[0] != prevmax:
ret.append([loc, -pq[0]])
return ret
위 코드에는 크나큰 결점이 하나 있다.
이는 heapq를 사용한 priority queue에서 원소 삭제가 O(N)이라는 것이다.
결과적으로 원소 삭제가 자주 일어날 경우, 위 코드는 현저히 느리다.
아래의 특수한 형태의 priority queue를 사용하면 원소 삭제가 O(logN)으로 가능하다.
https://focalpoint.tistory.com/228
Priority Queue - 시바견의 끄적임
Heapq만을 사용한 Priority Queue의 Time Complexity는 아래와 같다. Find max/min - O(1) Insert - O(logN) Remove - O(N) Remove Operation에 Linear Time이 필요하다는 것이 아쉽다. 이를 해결하기 위한 Custom..
focalpoint.tistory.com
from functools import cmp_to_key
import heapq
class PriorityQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.pq = []
self.removals = []
def insert(self, elem):
heapq.heappush(self.pq, -elem)
def getmax(self):
return -self.pq[0]
def remove(self, elem):
if elem == -self.pq[0]:
heapq.heappop(self.pq)
while self.removals and self.pq[0] == self.removals[0]:
heapq.heappop(self.pq)
heapq.heappop(self.removals)
else:
heapq.heappush(self.removals, -elem)
class Solution:
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
# [loc, height, isEnd]
points = []
for l, r, h in buildings:
points.append([l, h, 0])
points.append([r, h, 1])
def compare(p1, p2):
if p1[0] != p2[0]:
return p1[0] - p2[0]
if p1[2] != p2[2]:
return p1[2] - p2[2]
if p1[2] == 0:
return -(p1[1] - p2[1])
return p1[1] - p2[1]
points.sort(key=cmp_to_key(compare))
ret = []
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.insert(0)
for loc, height, isEnd in points:
prevmax = pq.getmax()
if not isEnd:
pq.insert(height)
if pq.getmax() != prevmax:
ret.append([loc, height])
else:
pq.remove(height)
if pq.getmax() != prevmax:
ret.append([loc, pq.getmax()])
return ret
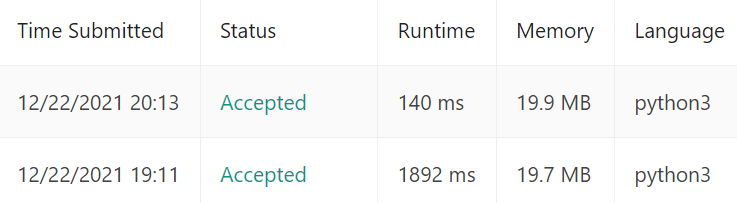
짜쟌~ Runtime이 1892ms -> 140ms로 개선되었다~!
'Computer Science > Coding Test' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LeetCode: 234. Palindrome Linked List (0) | 2021.12.24 |
|---|---|
| LeetCode: 239. Sliding Window Maximum (0) | 2021.12.23 |
| LeetCode: 206. Reverse Linked List (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| LeetCode: 202. Happy Number (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| LeetCode: 191. Number of 1 Bits (0) | 2021.12.21 |
